The Challenge: Greening a Green Industry
Hydropower is a cornerstone of renewable energy, yet the manufacturing of its components, from massive turbines to reinforced concrete dams, carries a significant environmental cost. The industry has traditionally relied on energy-intensive processes and materials with large carbon footprints. The core challenge was to systematically investigate, collate, and analyze modern, sustainable practices that could transform the entire manufacturing lifecycle.
This research aimed to create a holistic framework by reviewing existing literature on innovative approaches like Additive Manufacturing, sustainable material science, and comprehensive Life Cycle Assessments (LCA) to guide the industry toward a truly sustainable future.
My Role: Research Contributor & Co-Author
As a key member of this team, I played an integral role in the development and publication of this academic review. My responsibilities included:
- Literature Review & Synthesis: Conducted extensive searches of academic databases to identify key research on sustainable manufacturing, material science, and energy-efficient processes relevant to the hydropower sector.
- Framework Analysis: Analyzed and synthesized findings from diverse sources to help build a coherent framework, identifying trends, gaps, and best practices in the field.
- Content Contribution: Authored and co-authored specific sections of the paper, focusing on areas such as advanced manufacturing technologies and the role of regulatory standards.
- Collaborative Writing & Editing: Worked closely with fellow researchers to draft, review, and refine the manuscript for clarity, accuracy, and academic rigor, leading to its publication.
A Framework for Sustainability: Key Research Areas
This review did not involve direct simulation but instead focused on synthesizing existing data and case studies to identify three critical pillars for sustainable hydropower manufacturing.
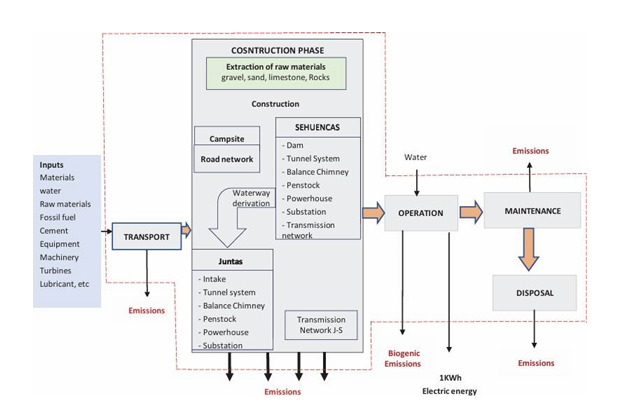
1. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)
A primary finding was the critical importance of adopting a cradle-to-grave perspective. LCA provides a holistic view of the environmental footprint, evaluating everything from raw material extraction and manufacturing to long-term operation and eventual decommissioning. Our review emphasized that a process-based LCA is essential for identifying the highest-impact areas and making data-driven decisions to enhance eco-efficiency.
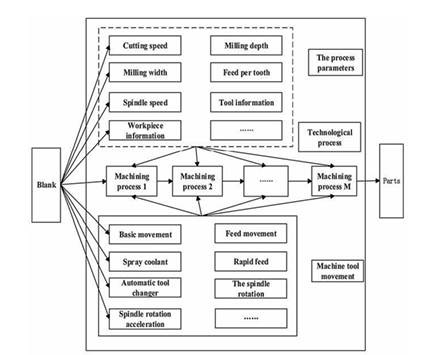
2. Advanced Manufacturing Processes
We identified a significant opportunity to reduce waste and energy consumption by moving beyond traditional methods. Technologies like **Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)** enable the creation of complex turbine parts with minimal material waste, while optimizing **CNC Machining** toolpaths and utilizing low-power states can drastically cut energy use. These innovations are key to making the manufacturing process both economically and environmentally viable.
3. Sustainable Material Selection
The materials used are central to the industry's environmental impact. Our research highlighted the benefits of using **recycled steel** for penstocks, developing **eco-efficient concrete** with recycled aggregates for dams, and deploying **bio-based lubricants** for hydraulic systems. These alternatives not only reduce carbon emissions but also minimize harm to aquatic ecosystems in case of leaks.
Conclusion & Project Impact
This research consolidates a wide range of strategies into a clear, actionable framework for sustainable manufacturing in the hydropower industry. By outlining the best practices in materials, processes, and lifecycle analysis, the paper serves as a valuable resource for engineers, policymakers, and industry stakeholders.
- Holistic Framework Developed: Produced a comprehensive review that synthesizes disparate research into a cohesive guide for sustainability.
- Key Technologies Identified: Highlighted the high-impact potential of advanced manufacturing and sustainable material science in reducing the industry's carbon footprint.
- Emphasized Policy & Standards: Underscored the crucial role of regulatory frameworks like ISO 14001 in driving industry-wide adoption of sustainable practices.
- Academic Contribution: Published in the IOP Conference Series, this work contributes to the academic discourse and provides a foundation for future research.
Ultimately, this project provides an intellectual blueprint for evolving the hydropower industry, ensuring that its contribution to a clean energy future is matched by an equally clean and responsible manufacturing ecosystem.